Co-ordinated DB Access (Thread-safe DB Access): Difference between revisions
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
(For the curious: Thread-safety is achieved by using a <code>[https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.threading.semaphoreslim(v=vs.100).aspx SemaphoreSlim]</code> Object (<code>FCoordinatedDBAccess</code>), two Methods that 'flip' the switch between protection/non-protection (<code>WaitForCoordinatedDBAccess</code> and <code>ReleaseCoordinatedDBAccess</code>) and by calling those two Methods appropriately in all places where it is required to achieve thread-safety across everything the <code>TDataBase</code> Class can do.) | (For the curious: Thread-safety is achieved by using a <code>[https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.threading.semaphoreslim(v=vs.100).aspx SemaphoreSlim]</code> Object (<code>FCoordinatedDBAccess</code>), two Methods that 'flip' the switch between protection/non-protection (<code>WaitForCoordinatedDBAccess</code> and <code>ReleaseCoordinatedDBAccess</code>) and by calling those two Methods appropriately in all places where it is required to achieve thread-safety across everything the <code>TDataBase</code> Class can do.) | ||
=====Automatic | =====Automatic Time-out (Stalling/Deadlock Protection)===== | ||
Suppose a thread that 'locks' the <code>TDataBase</code> Class (due to the thread-safety being in place) would run for a long time, or even 'stall' for some reason or the other, or get into an 'endless loop', and hence wouldn't release the 'lock' on the TDataBase class. While none of these should happen (of course...), the consequence of any of this happening would be that all other threads of a user that were waiting for DB Access would be waiting - for however long it takes - to get access to the DB. This situation would not only give the user the impression that 'OpenPetra isn't responding/has crashed', but would also mean they couldn't save any work that they haven't saved yet. An automatic time-out is in place to prevent those unwanted issues. This time-out applies not to the first thread (that 'locked' the <code>TDataBase</code> Class ), but to any 'next' thread that wants to use the <code>TDataBase</code> Class and which has to wait. The time-out means that this waiting isn't 'indefinite', but ends after a set time-out, and hence the thread that ran into the time-out can perform some action. That action could be as simple as repeating the request for DB access or giving the user the opportunity to either continue waiting or cancel the operation that the user initiated. | |||
'''TODO''' | '''TODO''' | ||
======Configuration (Optional): Timeout ====== | |||
<code>Server.DBWaitingTimeForCoordinatedDBAccess</code> | <code>Server.DBWaitingTimeForCoordinatedDBAccess</code> | ||
'''TODO''' | '''TODO''' | ||
Revision as of 14:07, 17 March 2015
THIS PAGE IS WORK IN PROGRESS
This page is currently being worked on. Please come back later to this page when you have been notified that it is finished!
Co-ordinated DB Access: Overview
The Problem it Solves
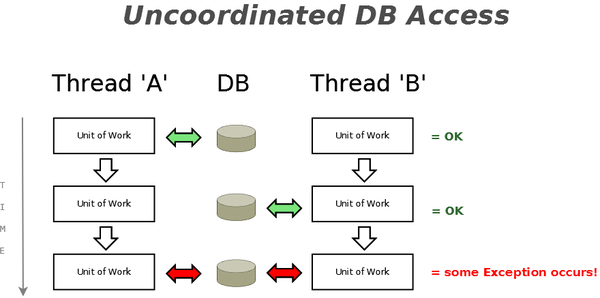
Before we had Co-ordinated DB Access in place, users ran into various Exceptions when multi-threaded DB access occurred - no matter whether that multi-threaded DB access was done intentionally/deliberately by the programmer, or whether it happened as something that resulted 'accidentally' because of an action the user took (and which we didn't prevent from happening). Co-ordinated DB Access not only prevents that from happening, but also provides new options to safely run program code that access the DB 'in parallel'.
The Solution
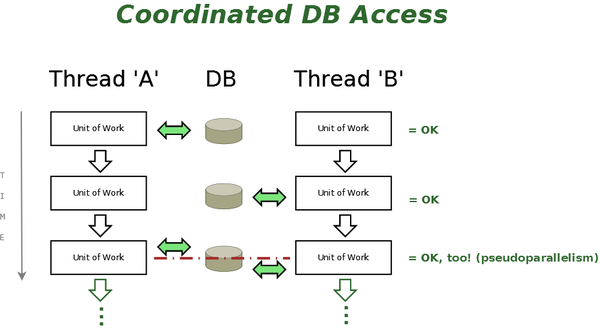
The primary solution was to make the TDataBase Class (OpenPetra's Database Access and Abstraction Layer) thread-safe (this got addressed by solving Bug #3852), meaning that we are employing pseudo-parallel Execution execution to prevent 'collisions' on DB Access. That in itself prevented the mentioned Exceptions from happening!
Building on that, ...
- provisions have been put in place to allow the OpenPetra software engineers to react programmatically to various new situations where the now co-ordinated DB Access can raise specific Typed Exceptions in case the desired 'parallel-ity' cannot be achieved automatically in a given situation;
- provisions have been made in the client-side 'Unhandled Exception Handler' to automatically show 'friendly and helpful' messages to the user when the software engineers didn't react programmatically to various new situations (yet).
It is expected that the automatic 'friendly and helpful' messages may well be enough for many situations - the ability to react programmatically to various new situations is merely there to allow for 'better' provisions for the user, e.g. to give Retry/Cancel options, or to prevent the user from taking certain actions in the first place that could (later) lead to the inability to take certain actions (e.g. disallowing the opening of a screen under certain circumstances because the circumstances would mean that any entered data could not be saved by the user later on).
Pseudo-parallel Execution
Pseudo-parallelism Definition
What happens is that we allow only one Thread at any given time access to DB-related functionality that is exposed through the TDataBase Class - that means that other Threads need to wait until one Thread is finished.
Sadly we can't offer 'true' parallelism, the reasons for that are:
- ADO.NET doesn't support this;
- PostgreSQL allows only one running DB Transaction per DB Connection.
Details of the Implementation
What is Done Automatically And What Needs to be Handled Manually
Automatic (and Fully Transparent): Thread-safe DB Access through the TDataBase Class
Automatic Thread-Safety
The thread-safety is fully transparent to the Software Engineer, that is, the software engineer doesn't need to do anything to make sure it works, and doesn't even know how it works.
(For the curious: Thread-safety is achieved by using a SemaphoreSlim Object (FCoordinatedDBAccess), two Methods that 'flip' the switch between protection/non-protection (WaitForCoordinatedDBAccess and ReleaseCoordinatedDBAccess) and by calling those two Methods appropriately in all places where it is required to achieve thread-safety across everything the TDataBase Class can do.)
Automatic Time-out (Stalling/Deadlock Protection)
Suppose a thread that 'locks' the TDataBase Class (due to the thread-safety being in place) would run for a long time, or even 'stall' for some reason or the other, or get into an 'endless loop', and hence wouldn't release the 'lock' on the TDataBase class. While none of these should happen (of course...), the consequence of any of this happening would be that all other threads of a user that were waiting for DB Access would be waiting - for however long it takes - to get access to the DB. This situation would not only give the user the impression that 'OpenPetra isn't responding/has crashed', but would also mean they couldn't save any work that they haven't saved yet. An automatic time-out is in place to prevent those unwanted issues. This time-out applies not to the first thread (that 'locked' the TDataBase Class ), but to any 'next' thread that wants to use the TDataBase Class and which has to wait. The time-out means that this waiting isn't 'indefinite', but ends after a set time-out, and hence the thread that ran into the time-out can perform some action. That action could be as simple as repeating the request for DB access or giving the user the opportunity to either continue waiting or cancel the operation that the user initiated.
TODO
Configuration (Optional): Timeout
Server.DBWaitingTimeForCoordinatedDBAccess
TODO
Semi-Automatic: (DB-)Call Retries
TODO
Configuration (Optional): Number of Retries
TODO
Automatic: Exception Handling in Case of Timeout
TODO
Examples
TODO
Manual: Exception Handling in Case of Timeout
TODO
Examples / Implementations
TODO
Challenges
TODO
The Future: A Safe-to-use, Multi-threading Enabled OpenPetra
TODO