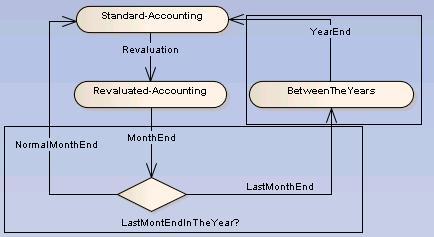
Periodic End Calculations
In Accounting Systems the term "Periodic End" either means a period like a month and or a period like a year. In "older systems" you also know the period of 10 years (deletion of old data) but actually we speak about the month and the year.
Today this two periods split the state of the accounting system into three different types.
Actually we speak about
- the standard accounting
- standard gift batches are allowed
- standard batches are allowed
- foreign currencies are allowed
- the revaluated accounting
- standard gift batches are allowed
- standard batches are allowed
- foreign currencies are allowed
- the year end accounting
- actually unknown ...
So:
- the month end only can change to the status "standard accounting" if it is a month of the same year or to "year end accounting" if the last month of the year has been closed.
- the year end has been done to set the value to the next year.
Info: The number of months can be lager than 12.
Month End
The month end will run the tests
- If a revaluation is done (i.e if the status "revaluated accounting" ist activated) (critical)
- If the system is not in the "year end accounting" (critical)
- If there are unposted batches (critical)
- If there are unposted gift batches (critical)
- If there are non zeroed suspense accounts (critical)
- If there are zeroed suspense accounts the user gets an informal message
The critical messages will disconnect any possibilities to continue.
The month end will include:
- Calculation of the admin fees (to be done)
- Calculation of the ICH fees (to be done)
- switch to the next month or to the "year end accounting" state
Year End
tbd.
RECONCILE – bank accounts, cash accounts and ICH account as normal. 2. STOCK - You will need to produce a summary of all literature stock at the year end, giving the number of each item and its value, indicating whether the items are for sale or for free distribution. Through the year you have included the previous year’s figure in the Balance Sheet, now a new figure is needed. 3. FIXED ASSETS - Depreciation for the year must be calculated and all entries done for assets acquired and disposed. Update your list of assets held at the year end, including any additions or disposals during the year. 4. CREDITORS AND DEBTORS - List of unpaid bills and any other outstanding creditors. Reconcile accounts payable and accounts receivable. 5. PREPAYMENTS AND ACCRUALS – Prepare schedules for all prepayments and accruals and put through the required entries to the General Ledger. 6. LOANS PAYABLE AND RECEIVABLE – Ensure that these balances are reconciled and the interest has been calculated correctly for the year. Ensure that these balances are correctly analysed between those falling due within one year and those due after one year. 7. SUSPENSE ACCOUNTS AND INTERNAL TRANSFERS – Reconcile these accounts and balances cleared out. 8. CURRENCY REVALUATIONS - If you have not always revalued foreign currency balances held then you must do it at the year end. 9. FUND BALANCE (EQUITY) - The balance on this account is not updated during the year but remains at the figure brought forward from last year. Now there will be a new figure. Whether or not you are able to handle year-end work, your AFO is always available to advise