Co-ordinated DB Access (Thread-safe DB Access): Difference between revisions
| (60 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Co-ordinated DB Access: Overview== | ==Co-ordinated DB Access: Overview== | ||
===The Problem it Solves=== | ===The Problem it Solves=== | ||
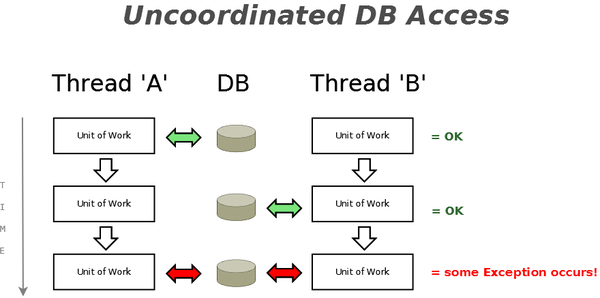
Before we had ''Co-ordinated DB Access'' in place, users ran into various Exceptions when multi-threaded DB access occurred - no matter whether that multi-threaded DB access was done intentionally/deliberately by the programmer, or whether it happened as something that resulted 'accidentally' because of an action the user took (and which we didn't prevent from happening). Co-ordinated DB Access not only prevents that from happening, but also provides | Before we had ''Co-ordinated DB Access'' in place, users ran into various Exceptions when multi-threaded DB access occurred on the same DB Connection - no matter whether that multi-threaded DB access was done intentionally/deliberately by the programmer, or whether it happened as something that resulted 'accidentally' because of an action the user took (and which we didn't prevent from happening). Co-ordinated DB Access not only prevents that from happening, but also provides options to safely run program code that attempts to access the DB in parallel on the same DB Connection (however, multi-threading always brings some challenges, esp. with DB access - for details read the [[Co-ordinated_DB_Access_(Thread-safe_DB_Access)#Challenges |Challenges]] section). | ||
[[File:Uncoordinated DB Access.png|600px|center|''Schematic diagram showing uncoordinated DB access'']] | [[File:Uncoordinated DB Access.png|600px|center|''Schematic diagram showing uncoordinated DB access'']] | ||
===The Solution=== | ===The Solution=== | ||
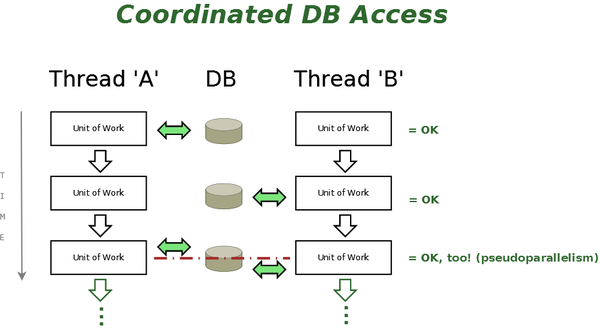
The primary solution was to make the <code>TDataBase</code> Class (OpenPetra's Database Access and Abstraction Layer) thread-safe (this got addressed by solving [https://tracker.openpetra.org/view.php?id=3852 Bug #3852]), meaning that we are employing [[Co-ordinated_DB_Access_(Thread-safe_DB_Access)#Pseudoparallel_Execution |pseudoparallel execution]] to prevent any 'collisions' on DB Access. That in itself prevented the Exceptions mentioned earlier from happening! | The primary solution was to make the <code>TDataBase</code> Class (OpenPetra's Database Access and Abstraction Layer) thread-safe (this got addressed by solving [https://tracker.openpetra.org/view.php?id=3852 Bug #3852]), meaning that we are employing [[Co-ordinated_DB_Access_(Thread-safe_DB_Access)#Pseudoparallel_Execution |pseudoparallel execution]] to prevent any 'collisions' on DB Access on the same DB Connection. That in itself prevented the Exceptions mentioned earlier from happening! (For 'true' parallel execution of DB Commands see [[Working with multiple DB Connections]]). | ||
[[File:Coordinated DB Access.png|600px|center|''Schematic diagram showing coordinated DB access'']] | [[File:Coordinated DB Access.png|600px|center|''Schematic diagram showing coordinated DB access'']] | ||
Building on that, ... | Building on that, ... | ||
* provisions have been put in place to allow the OpenPetra software engineers to react programmatically to various new situations where the now co-ordinated DB Access can raise specific Typed Exceptions in case the desired 'parallel-ity' cannot be achieved automatically in a given situation; | * provisions have been put in place to allow the OpenPetra software engineers to react programmatically to various new situations where the now co-ordinated DB Access can raise specific Typed Exceptions in case the desired 'parallel-ity' cannot be achieved automatically in a given situation (on a DB Connection that is shared by multiple Threads); | ||
* provisions have been made in the client-side 'Unhandled Exception Handler' to automatically show 'friendly and helpful' messages to the user when the software engineers didn't react programmatically to various new situations (yet). | * provisions have been made in the client-side 'Unhandled Exception Handler' to automatically show 'friendly and helpful' messages to the user when the software engineers didn't react programmatically to various new situations (yet). | ||
The automatic 'friendly and helpful' messages may well be enough for situations in which concurrent DB access operations aren't occurring often and where the user wouldn't be too annoyed to perform any retry attempts by themselves. | The automatic 'friendly and helpful' messages may well be enough for situations in which concurrent DB access operations aren't occurring often and where the user wouldn't be too annoyed to perform any retry attempts by themselves. [[Co-ordinated DB Access (Thread-safe DB Access)#Automatic:_Co-ordinated_DB_Access_Exception_Handling |Details]] | ||
The ability to react programmatically to the various new situations exists to perform automatic retries 'under the hood', to allow for 'better' provisions for the user (e.g. to provide Retry/Cancel options), and to be able to prevent the user from taking certain actions in the first place that could (later) lead to the inability to take certain actions (e.g. disallowing the opening of a screen under certain circumstances because the particular circumstance would mean that any entered data might not be 'save-able' by the user later on). | The ability to react programmatically to the various new situations exists to perform automatic retries 'under the hood', to allow for 'better' provisions for the user (e.g. to provide Retry/Cancel options), and to be able to prevent the user from taking certain actions in the first place that could (later) lead to the inability to take certain actions (e.g. disallowing the opening of a screen under certain circumstances because the particular circumstance would mean that any entered data might not be 'save-able' by the user later on). [[Co-ordinated DB Access (Thread-safe DB Access)#Manual:_Co-ordinated_DB_Access_Exception_Handling |Details]] | ||
====Pseudoparallel Execution==== | ====Pseudoparallel Execution==== | ||
What happens in our 'co-ordinated DB Access' is that we allow only one thread at any given time access to DB-related functionality that is exposed through the <code>TDataBase</code> Class. That means that other threads need to wait until the first thread has finished accessing the DB through the <code>TDataBase</code> Class (an automatic time-out [[Co-ordinated_DB_Access_(Thread-safe_DB_Access)#Automatic_Time-out_.28Thread_Stalling_Prevention.29 |time-out]] is in place to mitigate 'stalling' situations). | What happens in our 'co-ordinated DB Access' is that we allow only one thread at any given time access to DB-related functionality that is exposed through the <code>TDataBase</code> Class when those threads are ''sharing the same DB Connection''. That means that other threads that want to utilise the same DB Connection need to wait until the first thread has finished accessing the DB through the <code>TDataBase</code> Class (an automatic time-out [[Co-ordinated_DB_Access_(Thread-safe_DB_Access)#Automatic_Time-out_.28Thread_Stalling_Prevention.29 |time-out]] is in place to mitigate 'stalling' situations). | ||
We need to do this because we can't offer 'true' parallelism. The reasons for that are: | We need to do this because we can't offer 'true' parallelism on the ''sam''e DB Connection. The reasons for that are: | ||
* The ADO.NET DB driver model cannot maintain multiple active statements (commands) on a single DB Connection. | * The ADO.NET DB driver model cannot maintain multiple active statements (commands) on a single DB Connection. | ||
** (Well, for SQLServer and Oracle there is a specific solution {'Multiple Active Result Sets', [https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms131686.aspx | MARS]}, but it isn't a standard feature of ADO.NET and not available for other RDBMS's). | ** (Well, for SQLServer and Oracle there is a specific solution {'Multiple Active Result Sets', [https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms131686.aspx | MARS]}, but it isn't a standard feature of ADO.NET and not available for other RDBMS's). | ||
* even the PostgreSQL RDBMS allows only one running DB Transaction per DB Connection! | * even the PostgreSQL RDBMS allows only one running DB Transaction per DB Connection! | ||
For 'true' parallel execution of DB Commands see [[Working with multiple DB Connections]]! | |||
==Relation to [[Working with multiple DB Connections]]== | |||
Cf. [[Working with multiple DB Connections#Relation to Co-ordinated DB Access (Thread-safe DB Access) |this]] paragraph. | |||
==Details of the Implementation== | ==Details of the Implementation== | ||
| Line 37: | Line 39: | ||
The thread-safety is fully transparent to the software engineers, that is, the software engineers don't need to do anything to make sure it works, and don't even need to know how it works. | The thread-safety is fully transparent to the software engineers, that is, the software engineers don't need to do anything to make sure it works, and don't even need to know how it works. | ||
(For the curious: Thread-safety is achieved by using a <code>[https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.threading.semaphoreslim(v=vs.100).aspx SemaphoreSlim]</code> Object {<code>FCoordinatedDBAccess</code>} with a capacity of only one, two new Methods {<code>WaitForCoordinatedDBAccess</code> and <code>ReleaseCoordinatedDBAccess</code>}, and by calling those two Methods appropriately in all places where it is required to achieve thread-safety | (For the curious: Thread-safety is achieved by using a <code>[https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.threading.semaphoreslim(v=vs.100).aspx SemaphoreSlim]</code> Object {<code>FCoordinatedDBAccess</code>} with a capacity of only one, two new Methods {<code>WaitForCoordinatedDBAccess</code> and <code>ReleaseCoordinatedDBAccess</code>}, and by calling those two Methods appropriately in all places where it is required to achieve thread-safety 'inside' an instance of the <code>TDataBase</code> Class across every functionality that this Class offers. For the even-more-curious: A Mutex or lock couldn't be used to achieve that since these aren't 'thread-agnostic', whereas a SemaphoreSlim is thread-agnostic. Also, a SemaphoreSlim is a very performant way to achieve thread-safety. {[http://www.albahari.com/threading/part2.aspx#_Semaphore Details]}) | ||
=====Automatic Time-out (Thread Stalling Prevention)===== | =====Automatic Time-out (Thread Stalling Prevention)===== | ||
Suppose a thread that 'locks' the <code>TDataBase</code> Class (due to the thread-safety being in place) would run for a long time, or even 'stall' for some reason or the other, or get into an 'endless loop', and hence wouldn't release the 'lock' on the <code>TDataBase</code> Class. While none of these should happen (of course...), the consequence of any of this happening would be that all other threads of a user that were waiting for DB Access would be waiting to get access to the DB - for however long it takes for the first thread that 'grabbed the lock' to finish. | Suppose a thread that 'locks' an instance of the <code>TDataBase</code> Class (due to the thread-safety being in place) would run for a long time, or even 'stall' for some reason or the other, or get into an 'endless loop', and hence wouldn't release the 'lock' on that instance of the <code>TDataBase</code> Class. While none of these should happen (of course...), the consequence of any of this happening would be that all other threads of a user that were waiting for DB Access on that instance of <code>TDataBase</code> would be waiting to get access to the DB - for however long it takes for the first thread that 'grabbed the lock' to finish. In case the instance of <code>TDataBase</code> is the 'globally available' <code>DBAccess.GDBAccessObj</code> this situation would not only give the user the impression that 'OpenPetra isn't responding/has crashed', but would also mean they couldn't save any work that they haven't saved yet, which they might be able to do if we are able to offer them 'Retry/Cancel' options! | ||
An automatic time-out is in place to help avoid those unwanted issues. This time-out applies not to the first thread (that 'locked' the instance of the <code>TDataBase</code> Class), but to any 'next' thread that wants to use that instance of the <code>TDataBase</code> Class and which has to wait. The time-out means that this waiting isn't 'indefinite', but ends after a set time-out, and hence the thread that ran into the time-out can perform some action. That action could be as simple as repeating the request for DB access or giving the user the opportunity to either continue waiting or cancel the operation that the user initiated. | |||
''Important'': The time-out doesn't mean that a thread that wants to execute some action using the <code>TDataBase</code> Class has to wait until the automatic time-out has expired if another thread 'grabbed the lock' earlier. Rather, the second thread will execute the action as soon as the first thread finishes its work and 'releases the lock'! Example: If the first thread 'grabs the lock', executes an action and 'releases the lock' within 4 seconds, a second (waiting) thread will be able to 'grab the lock' after those 4 seconds, and not just after the time-out expired! | ''Important'': The time-out doesn't mean that a thread that wants to execute some action using the <code>TDataBase</code> Class has to wait until the automatic time-out has expired if another thread 'grabbed the lock' earlier on the same instance of <code>TDataBase</code>. Rather, the second thread will execute the action as soon as the first thread finishes its work and 'releases the lock'! Example: If the first thread 'grabs the lock', executes an action and 'releases the lock' within 4 seconds, a second (waiting) thread will be able to 'grab the lock' after those 4 seconds, and not just after the time-out expired! | ||
When the time-out does expire, the <code>TDataBase</code> Class throws | When the time-out does expire, the <code>TDataBase</code> Class throws an Exception, <code>EDBCoordinatedDBAccessWaitingTimeExceededException</code>. Though a calling Method could catch this Exception specifically, it is more helpful to catch its Base Class, <code>EDBAccessLackingCoordinationException</code>. For details about this see [[Co-ordinated_DB_Access_(Thread-safe_DB_Access)#Manual:_Co-ordinated_DB_Access_Exception_Handling |this]] section. | ||
======Configuration (Optional): Automatic Time-out ====== | ======Configuration (Optional): Automatic Time-out ====== | ||
| Line 52: | Line 55: | ||
====Semi-Automatic: (DB-)Call Retries==== | ====Semi-Automatic: (DB-)Call Retries==== | ||
The most common reaction to an automatic time-out should be a retry of getting the 'lock' on the <code>TDataBase</code> Class. The reason for that is that often the second or third attempt of getting this 'lock' succeeds (as many DB queries run only for a short time)! It would therefore not be very user-friendly to show a message to the user that the action that (s)he has taken could not be performed when an internal retry (which the user doesn't notice) can often succeed. | The most common reaction to an automatic time-out should be a retry of getting the 'lock' on a given instance of the <code>TDataBase</code> Class (e.g. on the 'globally available' <code>DBAccess.GDBAccessObj</code>). The reason for that is that often the second or third attempt of getting this 'lock' on that instance succeeds (as many DB queries run only for a short time)! It would therefore not be very user-friendly to show a message to the user that the action that (s)he has taken could not be performed when an internal retry on that instance (which the user doesn't notice) can often succeed. | ||
A new Class has been introduced to make it easy to program such DB call retries. The new <code>Ict.Common.DB.TServerBusyHelper</code> Class has got only one static Method, <code>CoordinatedAutoRetryCall</code>. Use this Method wherever you expect that the taking-out of a 'lock' on <code>TDataBase</code> could time out as other things that run in parallel might have come first in taking a 'lock' out. For details about this see section | A new Class has been introduced to make it easy to program such DB call retries. The new <code>Ict.Common.DB.TServerBusyHelper</code> Class has got only one static Method, <code>CoordinatedAutoRetryCall</code>. Use this Method wherever you expect that the taking-out of a 'lock' on a given instance of <code>TDataBase</code> could time out as other things that run in parallel on that instance might have come first in taking a 'lock' out. For details about this see [[Co-ordinated_DB_Access_(Thread-safe_DB_Access)#Manual:_Co-ordinated_DB_Access_Exception_Handling |this]] section. | ||
======Configuration (Optional): Number of Retries====== | ======Configuration (Optional): Number of Retries====== | ||
The number of retries that the <code>CoordinatedAutoRetryCall</code> Method automatically performs can be configured. That configuration option has been introduced to prevent users from running into time-outs too often in situations where an OpenPetra Site has got a slower server than average OpenPetra Sites, or a higher concurrent user count than average OpenPetra Sites, or both. The value would be set to a higher number than the default in such situations. | The number of retries that the <code>TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall</code> Method automatically performs can be configured. That configuration option has been introduced to prevent users from running into time-outs too often in situations where an OpenPetra Site has got a slower server than average OpenPetra Sites, or a higher concurrent user count than average OpenPetra Sites, or both. The value would be set to a higher number than the default in such situations. | ||
The time-out value defaults to 3 (=3 retries) but can be changed by including the appSetting <code>CoordinatedAutoRetryCallMaxRetries</code> in the Client.config file (for controlling the number of retries when the <code>CoordinatedAutoRetryCall</code> Method is used client-side) and/or the Server.config file (for controlling the number of retries when the <code>CoordinatedAutoRetryCall</code> Method is used server-side). | The time-out value defaults to 3 (=3 retries) but can be changed by including the appSetting <code>CoordinatedAutoRetryCallMaxRetries</code> in the Client.config file (for controlling the number of retries when the <code>TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall</code> Method is used client-side) and/or the Server.config file (for controlling the number of retries when the <code>CoordinatedAutoRetryCall</code> Method is used server-side). | ||
====Automatic: Co-ordinated DB Access Exception Handling==== | ====Automatic: Co-ordinated DB Access Exception Handling==== | ||
The client-side 'Unhandled Exception Handler' presents 'stock messages' to users in case an Exception that derives from the <code>EDBAccessLackingCoordinationException</code> Exception makes it as far as that (that is, if a programmer didn't use the <code>TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall</code> Method and didn't catch it server-side or client-side). This is a much better option than letting the Exception escalate and showing the Unhandled Exception Dialog as a result of that, | The client-side 'Unhandled Exception Handler' presents 'stock messages' to users in case an Exception that derives from the <code>EDBAccessLackingCoordinationException</code> Exception makes it as far as that (that is, if a programmer didn't use the <code>TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall</code> Method and didn't catch it server-side or client-side). This is a much better option than letting the Exception escalate and showing the Unhandled Exception Dialog as a result of that, and it can work on its own in many, simpler, scenarios. | ||
However, for complex OpenPetra operations, esp. ones where DB queries can take longer to run on a given instance of <code>TDataBase</code> (e.g. on the 'globally available' <code>DBAccess.GDBAccessObj</code>), custom code that reacts programmatically will need to be written in screens (or even server-side) to support the running of such features alongside Reports or Find screens, or to prevent users from launching such features in the first place - see [[Co-ordinated_DB_Access_(Thread-safe_DB_Access)#Manual:_Co-ordinated_DB_Access_Exception_Handling |this]] section for that. | |||
Example of such an automatically-shown MessageBox: | Example of such an automatically-shown MessageBox: | ||
| Line 69: | Line 73: | ||
OpenPetra Server Too Busy | OpenPetra Server Too Busy | ||
--------------------------- | --------------------------- | ||
The OpenPetra Server is currently too busy to perform the requested action. (Reason: | The OpenPetra Server is currently too busy to perform the requested action. (Reason: Waiting time for initiating exclusive data access exceeded.). | ||
Please wait a few seconds, then retry the action that you wanted to perform (if you had previously started a long-running action and this is not finished yet, you might need to wait until this is finished). | Please wait a few seconds, then retry the action that you wanted to perform (if you had previously started a long-running action and this is not finished yet, you might need to wait until this is finished). | ||
| Line 78: | Line 82: | ||
--------------------------- | --------------------------- | ||
The '(Reason: XXX.)' part in those Messages can have different wording that helps a developer to know what has | The '(Reason: XXX.)' part in those Messages can have different wording that helps a developer to know what has gone wrong (since the the Exception information is 'hidden' from the GUI): | ||
* 'Reason: Waiting time for initiating exclusive data access exceeded.' – gets shown when <code>EDBTransactionBusyException</code> gets thrown. This will be the case when the caller called one of the <code> | * 'Reason: Waiting time for initiating exclusive data access exceeded.' – gets shown when <code>EDBTransactionBusyException</code> gets thrown. This will be the case when the caller called one of the <code>BeginXXXTransaction</code> Methods, but another DB Transaction (e.g. from running a Report) was already running on the same <code>TDataBase</code> instance and the call cannot be satisfied because no second (=concurrent) DB Transaction can be started. | ||
* 'Reason: Failed to initiate shared data access.' – gets shown when <code>EDBTransactionIsolationLevelWrongException</code> gets thrown. This will be the case when the caller called one of the <code>GetNewOrExistingXXXTransaction</code> Methods, but another DB Transaction (e.g. from running a Report) was already running and the call cannot be satisfied because of a mismatch of the 'IsolationLevel'. | * 'Reason: Failed to initiate shared data access.' – gets shown when <code>EDBTransactionIsolationLevelWrongException</code> gets thrown. This will be the case when the caller called one of the <code>GetNewOrExistingXXXTransaction</code> Methods, but another DB Transaction (e.g. from running a Report) was already running on the same <code>TDataBase</code> instance and the call cannot be satisfied because of a mismatch of the 'IsolationLevel'. | ||
* 'Reason: Waiting time for data access exceeded.' – gets shown when the new <code>EDBCoordinatedDBAccessWaitingTimeExceededException</code> gets thrown. This will be the case when the caller called one of the <code>GetNewOrExistingXXXTransaction</code> Methods, but another DB Transaction (e.g. from running a Report) was already running, and – while there wasn't a mismatch of the IsolationLevel – the second call timed out because it could not get exclusive access to the DB. This will be the case when the original call to the DB takes longer than the time-out (3 seconds by default). | * 'Reason: Waiting time for data access exceeded.' – gets shown when the new <code>EDBCoordinatedDBAccessWaitingTimeExceededException</code> gets thrown. This will be the case when the caller called one of the <code>GetNewOrExistingXXXTransaction</code> Methods, but another DB Transaction (e.g. from running a Report) was already running on the same <code>TDataBase</code> instance, and – while there wasn't a mismatch of the IsolationLevel – the second call timed out because it could not get exclusive access to the DB Connection that is held open by that <code>TDataBase</code> instance. This will be the case when the original call to the DB (on the same <code>TDataBase</code> instance) takes longer than the time-out (3 seconds by default). | ||
Additionally, when the appSetting '<code>Client.DebugLevel</code>' is set to a minimum of 3 in the Client.config file the Unhandled Exception handler also logs the full Exception details to the Client.log. ''This is useful for detailed checks by the developer''. At that DebugLevel the developer also gets information in the Client.log about the various retry attempts, and if they were exceeded, for cases where screens handle those using the in an automatic retry fashion by means of the <code>TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall</code> Method. Examples of screens/screen parts for the latter: the Partner Find/Partner Info Panel, the Partner Edit screen and the Maintain Extracts screen (when opening a Partner from the latter). The Client-side Cacheable DataTable Manager utilises <code>TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall</code>, too. | Additionally, when the appSetting '<code>Client.DebugLevel</code>' is set to a minimum of 3 in the Client.config file the Unhandled Exception handler also logs the full Exception details to the Client.log. ''This is useful for detailed checks by the developer''. At that DebugLevel the developer also gets information in the Client.log about the various retry attempts, and if they were exceeded, for cases where screens handle those using the in an automatic retry fashion by means of the <code>TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall</code> Method. Examples of screens/screen parts for the latter: the Partner Find/Partner Info Panel, the Partner Edit screen and the Maintain Extracts screen (when opening a Partner from the latter). The Client-side Cacheable DataTable Manager utilises <code>TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall</code>, too. | ||
=====Examples===== | =====Examples===== | ||
Apart from the example that is shown in the bullet list below there aren't any specific example actions that you could take to make the automatic 'stock messages' come up; rather, they will come up when an <code>EDBAccessLackingCoordinationException</code> Exception makes it as far as the Unhandled Exception Handler! | Apart from the example that is shown in the bullet list below there aren't any specific example actions that you could take to make the automatic 'stock messages' come up; rather, they will come up when an <code>EDBAccessLackingCoordinationException</code> Exception makes it as far as the Unhandled Exception Handler! (You can try to 'provoke' such an occurrence, though, by following the instructions [[Co-ordinated DB Access (Thread-safe DB Access)#How_to_Find_Out_if_.28Automatic.29_Co-ordinated_DB_Access_Will_Yield_Acceptable_Behaviour_In_a_Given_Circumstance |here]].) | ||
Reproducible example for a <code>BeginXXXTransaction</code> call 'not going through': | Reproducible example for a <code>BeginXXXTransaction</code> call 'not going through' on the 'globally available' <code>DBAccess.GDBAccessObj</code>: | ||
* Start the 'Partner by Subscription' Report from Partner Module -> Reports with a 'popular' Subscription (e.g. 'AFRIKAANS' on the SA DB; that will run for quite some time). | * Start the 'Partner by Subscription' Report from Partner Module -> Reports with a 'popular' Subscription (e.g. 'AFRIKAANS' on the SA DB; that will run for quite some time). | ||
* ''While that runs'', go to Partner Module -> Partners and click 'Add New Person'. The screen opens fine, but on clicking 'OK' the user is presented with an automatically-shown MessageBox (see example above). On clicking 'OK' on that MessageBox, the user is back in the Main Menu (while the Report happily continues to calculate!). That also works when 'New Partner' is initiated e.g. from the Partner Edit screen, in that case one is back on the Partner Edit screen that you pressed 'New Partner' on. | * ''While that runs'', go to Partner Module -> Partners and click 'Add New Person'. The screen opens fine, but on clicking 'OK' the user is presented with an automatically-shown MessageBox (see example above). On clicking 'OK' on that MessageBox, the user is back in the Main Menu (while the Report happily continues to calculate!). That also works when 'New Partner' is initiated e.g. from the Partner Edit screen, in that case one is back on the Partner Edit screen that you pressed 'New Partner' on. | ||
** We might be able to improve on this by keeping the user in the 'New Partner' Dialog (rather than closing this and returning him/her to wherever (s)he came from), but that is something that needs extra assessment and specific programming. | ** We might be able to improve on this by keeping the user in the 'New Partner' Dialog (rather than closing this and returning him/her to wherever (s)he came from), but that is something that needs extra assessment and specific programming. | ||
** | ** Notes | ||
*** In this case a <code>BeginXXXTransaction</code> call with IsolationLevel 'Serializable' needs to be used because only that can guarantee that the Partner Key that gets generated will exist exactly once in the DB! | |||
*** The solution to overcome this particular issue is to use the [[Working with multiple DB Connections]] feature in the Partner Edit UIConnector (<code>TPartnerEditUIConnector</code> Class)! | |||
====Manual: Co-ordinated DB Access Exception Handling==== | ====Manual: Co-ordinated DB Access Exception Handling==== | ||
Manual handling of Exceptions that either stem from co-ordinated DB Access, or from calling one of the <code>BeginXXXTransaction</code> Methods when a DB Transaction is already running is done in several ways: | Manual handling of Exceptions that either stem from co-ordinated DB Access, or from calling one of the <code>BeginXXXTransaction</code> Methods when a DB Transaction is already running is done in several ways: | ||
===== Utilising the <code>TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall</code> Method ===== | |||
Usage: Performing 'silent' and automatic retries for 'getting a lock' on an instance of the <code>TDataBase</code> Class (e.g. on the 'globally available' <code>DBAccess.GDBAccessObj</code> <code>TDataBase</code> instance). Use this where you expect (or know) that multi-threaded DB Access on an instance of the <code>TDataBase</code> Class may potentially occur due to user actions or deliberate programmatic means. | |||
======What The Method Does====== | |||
The <code>TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall</code> Method will automatically execute program code that resides in a Delegate ''at least once'', but ''up to'' 'n' times when required. It will repeat the execution of that program code in case either the <code>EDBTransactionBusyException</code>, the <code>EDBCoordinatedDBAccessWaitingTimeExceededException</code> or the <code>EDBAttemptingToWorkWithTransactionThatGotStartedOnDifferentThreadException</code> (see [https://wiki.openpetra.org/index.php/Working_with_multiple_DB_Connections#Performing_Automatic_Retries_When_EDBAttemptingToWorkWithTransactionThatGotStartedOnDifferentThreadException_Gets_Thrown here] for the latter) Exceptions get thrown (all those Exceptions derive from <code>EDBAccessLackingCoordinationException</code>). | |||
''' | '''Retry Strategy''' | ||
* in | * Repeats are performed up to a set number of times (how often it is repeated at most is dermined by a default value {3} or the optional appSetting <code>CoordinatedAutoRetryCallMaxRetries</code> in the Client.config or Server.config file. [[Co-ordinated DB Access (Thread-safe DB Access)#Configuration_.28Optional.29:_Number_of_Retries |Details]]); | ||
'' | * The Method doesn't wait between the retries but issues a retry attempt immediately after one of the Exceptions mentioned in the previous paragraph gets thrown; | ||
* By default the Method doesn't do anything when the number of repeats got exceeded, but it can be instructed to throw an <code>EDBAutoServerCallRetriesExceededException</code> Exception in that case by setting the optional Argument <code>AWhenNotSuccessfulThrowSpecialException</code> to <code>true</code>. That is normally not necessary, though, as you will find out in the next section. | |||
That Method can be used ''client-side or server-side''. While it does the same on both 'sides', the scenarios in which you would want to use it client-side or server-side differ. | |||
* Client-side | |||
** Usage: Performing retries 'silently'. In case the retry attempts were exceeded the user should get told that either... | |||
*** the action the user wanted to take cannot be performed because the server is busy at the moment and that the user will need to try that action again at a later time. | |||
*** the action the user wanted to take cannot be performed because the server is busy at the moment and the user is given the choice to either retry or to cancel the action (this is of course more user-friendly, but it might not always be easy to implement). | |||
* Server-side | |||
** Usage: Performing retries 'silently'. In case the retry attempts were exceeded an appropriate action should get taken by the server-side code. | |||
======How to Use The Method====== | |||
This is best explained by showing client-side example code: | |||
bool ServerCallSuccessful = false; | |||
IMyUIConnector UIConnector = null; | |||
... | |||
Ict.Common.DB.TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall("''Some Context (only used for logging)''", ref ServerCallSuccessful, | |||
delegate | |||
{ | |||
UIConnector = TRemote.''SomeServerCall''(); | |||
ServerCallSuccessful = true; | |||
}); | |||
if (!ServerCallSuccessful) | |||
{ | |||
// ServerCallRetries must be equal to the maximum number of retries when we get here! | |||
if (TServerBusyHelperGui.ShowServerBusyDialogWhenOpeningForm(Catalog.GetString("''Some Context That is Meaningful to the User Here''")) == DialogResult.Retry) | |||
{ | |||
// In the simplest case: recursively call the Method that this code snippet is in... | |||
} | |||
return; // Also gets executed when the user chooses 'Cancel' in the displayed dialog! | |||
} | |||
// Further program code continues execution only if there were no retry attempts, or if the last retry attempt succeeded. | |||
'''Important''': The code section inside the Delegate code block is responsible for setting <code>ServerCallSuccessful = true;</code>, as only this section can know whether the server call went through OK, or not. The <code>Ict.Common.DB.TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall</code> Method evaluates the value of this Variable and will issue retries until either the Variable's value becomes <code>true</code> or the number of maximum retries has been exceeded. | |||
Once the <code>Ict.Common.DB.TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall</code> returns, the program code that called this Method must evaluate the value of the <code>ServerCallSuccessful</code> Variable to find out whether the server call succeeded (with, or without retries) or failed and needs to take appropriate action. | |||
As for the action to take when the server call didn't succeed: The <code>TServerBusyHelperGui</code> Class has been introduced to provide a small library that facilitates the uniform display of MessageBoxes and retry/cancel options. Have a look at the available Methods and choose the one that you want to implement in your code section. | |||
If you call the <code>TServerBusyHelperGui.ShowServerBusyDialogWhenOpeningForm</code> Method the user has the choice between retry or cancel. To make the 'retry' option viable you might need to refactor the server call out of existing code into a Method of its own so it can get called recursively for the retries. | |||
A good place on the client side in which to put the call to <code>Ict.Common.DB.TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall</code> is the <code>Form.Load</code> event. There the cancellation of the opening of the form might be easiest as well. | |||
Any server-side use of the <code>Ict.Common.DB.TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall</code> is very similar to what is shown above, though the <code>TServerBusyHelperGui</code> Class isn't available server-side. | |||
The <code>Ict.Common.DB.TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall</code> Method has two optional Arguments, <code>bool AWhenNotSuccessfulThrowSpecialException</code> and <code>string AExceptionMessage</code>. The program code as explained above is rather elegant, but in case you rather want an Exception to be raised when the retry attempts were exceeded, you can make the Method raise the Typed Exception <code>EDBAutoServerCallRetriesExceededException</code> by supplying <code>true</code> to the <code>AWhenNotSuccessfulThrowSpecialException</code> Argument. If you do that, then setting <code>AExceptionMessage</code> will allow passing a Message to that Exception. | |||
=====Catching <code>EDBAccessLackingCoordinationException</code> Server-side===== | |||
<code>EDBAccessLackingCoordinationException</code> is the Base Class from which the following Exceptions derive: | |||
* <code>EDBTransactionIsolationLevelWrongException</code> | |||
* <code>EDBTransactionBusyException</code> | |||
* <code>EDBCoordinatedDBAccessWaitingTimeExceededException</code> | |||
* <code>EDBAutoServerCallRetriesExceededException</code> | |||
If you have an Exception handler in place in server-side code that logs all Exceptions and then throws the Exception up the call stack you will likely not want to log the occurrence of any of the above Exceptions as the client side can deal with those in a good way (either you handle it programmatically or the 'Unhandled Exception Handler' will show a 'stock message' as the last resort). To prevent any of those Exceptions from getting logged, add a code section like the following ''before'' the <code>catch (Exception)</code> code section: | |||
catch (EDBAccessLackingCoordinationException) | |||
{ | |||
// don't log this Exception - the Client knows how to deal with it. | |||
throw; | |||
} | |||
=====Examples / Implementations===== | =====Examples / Implementations===== | ||
| Line 110: | Line 184: | ||
======Client Side====== | ======Client Side====== | ||
''This section needs reviewing as we expect that we will use [[Working with multiple DB Connections | multiple DB Connections]] in several of the places mentioned!'' | |||
* Partner Edit screen (Method 'GetPartnerEditUIConnector' in file \csharp\ICT\Petra\Client\MPartner\Gui\PartnerEdit.ManualCode.cs); | * Partner Edit screen (Method 'GetPartnerEditUIConnector' in file \csharp\ICT\Petra\Client\MPartner\Gui\PartnerEdit.ManualCode.cs); | ||
* Maintain Extracts screen - when opening a Partner for editing (Method 'EditPartner' in file \csharp\ICT\Petra\Client\MPartner\Gui\Extracts\UC_ExtractMaintain.ManualCode.cs); | * Maintain Extracts screen - when opening a Partner for editing (Method 'EditPartner' in file \csharp\ICT\Petra\Client\MPartner\Gui\Extracts\UC_ExtractMaintain.ManualCode.cs); | ||
| Line 115: | Line 192: | ||
* 'TSystemDefaults.GetSystemDefault' Method in file \csharp\ICT\Petra\Client\app\Core\SystemDefaults.cs; | * 'TSystemDefaults.GetSystemDefault' Method in file \csharp\ICT\Petra\Client\app\Core\SystemDefaults.cs; | ||
* 'TFrmMainWindowNew.UpdateSubsystemLinkStatus' Method in file \csharp\ICT\Petra\Client\app\MainWindow\MainWindowNew.ManualCode.cs. | * 'TFrmMainWindowNew.UpdateSubsystemLinkStatus' Method in file \csharp\ICT\Petra\Client\app\MainWindow\MainWindowNew.ManualCode.cs. | ||
** this gets called every time a users switches to the Finance Module in the Main Menu. The retries are there as the user might do that while other things are running against the DB (e.g. a Partner Find search operatin, or a FastReport). | |||
The Client-side CacheableDataTable Manager (TDataCache) utilises <code>TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall</code>, too (two overloads of the Method 'GetCacheableDataTableFromPetraServer' in file \csharp\ICT\Petra\Client\app\Core\Cache.cs). | The Client-side CacheableDataTable Manager (TDataCache) utilises <code>TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall</code>, too (two overloads of the Method 'GetCacheableDataTableFromPetraServer' in file \csharp\ICT\Petra\Client\app\Core\Cache.cs). | ||
======Server Side====== | ======Server Side====== | ||
''This section needs reviewing as we expect that we will use [[Working with multiple DB Connections | multiple DB Connections]] in several of the places mentioned!'' | |||
* 'TReportingDbAdapter.RunQuery' Method in file \csharp\ICT\Petra\Server\lib\MCommon\Main.cs; | * 'TReportingDbAdapter.RunQuery' Method in file \csharp\ICT\Petra\Server\lib\MCommon\Main.cs; | ||
** This is used by FastReports for executing arbitrary SQL statements | |||
* 'TSystemDefaults.GetSystemDefault'''s'''' Method in file \csharp\ICT\Petra\Server\lib\MSysMan\SystemDefaults.cs. | * 'TSystemDefaults.GetSystemDefault'''s'''' Method in file \csharp\ICT\Petra\Server\lib\MSysMan\SystemDefaults.cs. | ||
==Extra Things that You Need to Know== | |||
===How to Find Out if (Automatic) Co-ordinated DB Access Will Yield Acceptable Behaviour In a Given Circumstance=== | |||
It can be trick to try to exercise the program code that you have written manually for the retrying of server calls that make DB calls, as it will only run when the co-ordinated DB Access retries have been 'used up' on an instance of the <code>TDataBase</code> Class (e.g. on the 'globally available' <code>DBAccess.GDBAccessObj</code> <code>TDataBase</code> instance). | |||
Connecting the PetraServerConsole.exe to a DB that is remotely located rather than on your local development machine will greatly increase the likelihood that your code will get run. | |||
Other ways of 'helping' that to occur is to use either one, or both, of the following <code>appSetting</code>s: | |||
* Place <code>CoordinatedAutoRetryCallMaxRetries</code> in the appropriate config file (Client.config or Server.config) and set its value to '1', meaning only one call attempt is made, and if this times out, no further retries will be made. | |||
** This will raise the likelihood of running into a time-out and the calling Method's code path that deals with non-successful server calls will be more likely run because of this. ([[Co-ordinated DB Access (Thread-safe DB Access)#Configuration_.28Optional.29:_Number_of_Retries |Details]]) | |||
* Place <code>Server.DBWaitingTimeForCoordinatedDBAccess</code> in the Server.config file and setting its value to something quite low, such as 50 (the default is 3000). The value specifies the number of milliseconds a second thread will wait for the first thread to be releasing the 'lock' on an instance of the <code>TDataBase</code> Class (e.g. on the 'globally available' <code>DBAccess.GDBAccessObj</code> <code>TDataBase</code> instance). | |||
** The lower the number, the more the likelihood of running into a time-out is raised and the calling Method's code path that deals with non-successful server calls will be more likely run because of this. ([[Co-ordinated DB Access (Thread-safe DB Access)#Configuration_.28Optional.29:_Automatic_Time-out |Details]]) | |||
===Programming / Debugging === | |||
* '<code>return</code>' statements can be placed inside the code section that becomes a 'delegate', but they leave ''that'' code section and not the Method that contains the Automatic Transaction, and only a '<code>return''';'''</code>' statement that doesn't return a value is possible. | |||
* The code section that becomes a 'delegate' must not use '<code>ref</code>' or '<code>out</code>' Arguments of the Method that they are contained in (as that will result in the C# Compiler Error CS1628) | |||
** Solution: Declare a local Variable and assign the value of a '<code>ref</code>' or '<code>out</code>' Argument to it, then use the local Variable in the code section that becomes a 'delegate'. (In case of a '<code>ref</code>' Argument you will likely need to assign the value of that Variable to the Argument before you leave the Method in order for the Argument to have the same value than the Variable.) | |||
*** Note: By assigning the value to the local Variable, the local Variable points to the same address in memory than the value of the '<code>ref</code>' or '<code>out</code>' Argument - hence they are referencing the same instance of the object. This is an implementation detail of C# (this is the same as with Java). | |||
* Debugging: | |||
** There is some extra code to step through if one single-steps into/out of a code section that becomes a 'delegate' (compared to the code that follows the try/finally Policy and that doesn't use the Automatic DB Transaction Handling) | |||
*** Solution if you don't want that to happen: | |||
**** Use 'Step over' (F10) instead of 'Step into' (F11) on those code lines. | |||
**** In case you use SharpDevelop: Put a breakpoint on the line in the delegate from where on you want to investigate as F10 steps over the entire code that is contained in the delegate if this isn't done! | |||
** ''As the software engineer can step into the program code of any of the new Methods that handle the automatic DB Transactions (s)he can see as to why the DB Commits/DB Rollbacks happen!'' | |||
** When using SharpDevelop 5 to halt debug execution at the 'Automatic DB Handling' scope the whole code section is highlighted in yellow - very helpful, as the scope of the DB access logic is easily seen through that :-) | |||
* Logging | |||
** The logging facilities of the <code>TDataBase</code> Class have been improved and extended when Co-ordinated DB Access got implemented. | |||
*** Specifically, Thread ID's, Thread Names (where available) and AppDomains get logged in all situations where one needs that information while debugging program code that deals with multiple threads. Also, StackTraces have been added here and there to help developers figure out what happens. | |||
*** At the new DebugLevel 11 even more StackTraces get logged, namely whenever a 'lock' is taken out on an instance of the <code>TDataBase</code> Class (e.g. on the 'globally available' <code>DBAccess.GDBAccessObj</code> <code>TDataBase</code> instance), and when it is released. You will find that this is extremely verbose and hence it should only be used while debugging very tricky program code that deals with multiple threads. | |||
==Challenges== | ==Challenges== | ||
===<code>GetNewOrExistingXXXTransaction</code> Must be Used When Multiple Threads Need 'Parallel' DB Access=== | |||
When multiple threads are to be running side-by-side and both will be accessing the DB with the same instance of the <code>TDataBase</code> Class (e.g. using the 'globally available' <code>DBAccess.GDBAccessObj</code> <code>TDataBase</code> instance), all code sections in both threads' server-side program code must start or re-use DB Transactions by calling <code>GetNewOrExistingXXXTransaction</code>. This means that none of the code sections in both threads' server-side code must call <code>BeginXXXTransaction</code>. The obvious reason for that is that we can't start a second DB Transaction as we are employing [[Co-ordinated_DB_Access_(Thread-safe_DB_Access)#Pseudoparallel_Execution |pseudoparallel execution]]. (For 'truly' parallel DB Transaction and true parallel execution of DB Commands, which get around that limitation, see [[Working with multiple DB Connections]]). | |||
====IsolationLevels Need To be Fitting When Multiple Threads Need 'Parallel' DB Access==== | |||
In addition to what the previous paragraph stated, all code sections in both threads' server-side program code must be using the same IsolationLevel in the <code>GetNewOrExistingXXXTransaction</code> calls, as otherwise an <code>EDBTransactionIsolationLevelWrongException</code> Exception will be thrown at some point by one of the <code>GetNewOrExistingXXXTransaction</code> calls. (For 'truly' parallel DB Transaction and true parallel execution of DB Commands, which get around that limitation, see [[Working with multiple DB Connections]]). | |||
===Performance Considerations=== | ===Performance Considerations=== | ||
As we are employing [[Co-ordinated_DB_Access_(Thread-safe_DB_Access)#Pseudoparallel_Execution |pseudoparallel execution]] to prevent any 'collisions' on DB Access, you must expect that DB access is a limiting factor in how 'parallel' multiple threads can actually run, even on servers that have multiple processors! | As we are employing [[Co-ordinated_DB_Access_(Thread-safe_DB_Access)#Pseudoparallel_Execution |pseudoparallel execution]] to prevent any 'collisions' on DB Access on the same instance of the <code>TDataBase</code> Class (e.g. on the 'globally available' <code>DBAccess.GDBAccessObj</code> <code>TDataBase</code> instance), you must expect that DB access is a limiting factor in how 'parallel' multiple threads can actually run, even on servers that have multiple processors! (For 'truly' parallel DB Transaction and true parallel execution of DB Commands, by which we ''can get around that 'bottleneck''', see [[Working with multiple DB Connections]]!) | ||
How much the pseudoparallel execution will impede the performance of multiple threads that are accessing the DB with the same instance of the <code>TDataBase</code> Class will depend heavily on how much the individual threads utilise DB access vs. how much they 'compute', i.e. perform non-DB-access-related operations. If both threads access the DB heavily at roughly the same times, the execution speed of the threads will be heavily impeded as only one thread a time gets access to the DB. If, however, the threads do quite some computations and only some DB access (which ideally doesn't occur at roughly the same times) then the performance of individual multiple threads will not be impeded and operations involving multiple threads can well yield advantages over operations that consist of a single thread on servers that have multiple processors. | |||
This ''also affects the user'': When a user starts multiple Reports in parallel (e.g. just before going on lunch break), the combined time that both Reports take to calculate might be higher, or lower, than if they were started individually one-after-the-other. This will depend on how many DB access operations will 'compete' over DB access on the same instance of the <code>TDataBase</code> Class (e.g. on the 'globally available' <code>DBAccess.GDBAccessObj</code> <code>TDataBase</code> instance) - and of course also whether the server on which the PetraServerConsles.exe process runs has got multiple processors, or only one processor... | |||
===Stopping/Cancellation of Multiple Running Queries=== | |||
Reference: [[Stopping_of_Running_DB_Queries |Stopping of Running DB Queries]] | |||
''This section needs reviewing as we expect that we will use [[Working with multiple DB Connections | multiple DB Connections]] in several of the places mentioned!'' | |||
When multiple DB actions are running in a [[Co-ordinated_DB_Access_(Thread-safe_DB_Access)#Pseudoparallel_Execution |pseudoparallel fashion]] on the same instance of the <code>TDataBase</code> Class (e.g. using the 'globally available' <code>DBAccess.GDBAccessObj</code> <code>TDataBase</code> instance), the behaviour of a cancellation action is as follows: | |||
* Pressing 'Cancel' on the Partner Find screen while a FastReport is running, or pressing 'Cancel' on a FastReport Report Window while Partner Find is running ''can'' work when the particular FastReport that runs has proper error handling and cancellation handling; the 'Income Expense Report' does have that (at least in some of the main areas of the report code...). When it works, both the FastReport and the Find screen stop their queries ''at the same time''. By the time of writing this we are not sure why this happens, but this might be down to the Npgsql ADO.NET PostgreSQL driver, or even down to PostgreSQL. | |||
* Pressing 'Cancel' on the Partner Find screen while a FastReport is running can in certain circumstances also break OpenPetra, at least at the time of writing. This will need further investigation, but again this might not be something that we can provide safely in the future (hence we might need to prevent that in the GUI 'somehow'). However, getting this to work is probably not very high on our list of things that we will implement in the nearer future... | |||
===Running Multiple XML Reports in Parallel: To be Investigated Further=== | |||
<s>It is at present not possible to start another XML Report (=non-FastReport) while a XML Report is already calculating. | |||
= | The one reason for that has been identified so far is that our Logging framework (which is used for the output to the StatusBar) isn’t thread-safe and any such attempt results in a <code>NullReferenceException</code> for that reason. | ||
That needs to be looked into specifically.</s> This has been fixed by ChristianK (this was Bug [https://tracker.openpetra.org/view.php?id=4489 #4489])! | |||
Once that is solved (''is is now!'') it is thought that we will likely encounter further 'stumbling blocks' for parallel XML Report runs, though (one example: Bug [https://tracker.openpetra.org/view.php?id=4481 #4481]). This will need further investigation, but this might not be something that we can provide safely in the future (hence we might need to prevent that in the GUI 'somehow'). However, getting this to work is probably not very high on our list of things that we will implement in the nearer future... | |||
===''' | ===Running multiple FastReports in Parallel=== | ||
''This section needs reviewing as we expect that we will be able to utilise a separate DB Connection for each FastReport Report instance (see [[Working with multiple DB Connections]])!'' | |||
In principle multiple FastReport Reports can be run at the same time. | |||
* ChristianK succeeded in running the Finance Module -> General Ledger -> 'Income Expense Statement' Report and the 'Excecutive Summary' Report in parallel. | |||
* This might well not work with all kinds of combinations of FastReports - thorough Exception handling in the Reports' program code (and Cancellation handling, too, in case the 'Cancel' Button gets pressed on the Report Form or on another Form that has got a 'Cancel' button) is a must for that to work properly! | |||
===Multi-threading: General Advice=== | ===Multi-threading: General Advice=== | ||
General caution/advice: Programming with multiple threads is always much, much harder than programming with a single thread. When multiple threads access the same program data (Fields, static Fields, structs, etc.) one can easily get intermittent problems which can be very hard to pin-point and to resolve. Extreme diligence needs to be employed when multiple threads should access some shared program data in a writing fashion! Debugging a multi-threaded program is also considerably more difficult than debugging a single-threaded program. Whole books are devoted to the topic of multi-threaded programming as multi-threading is a quite difficult discipline that is hard to master... | General caution/advice: Programming with multiple threads is always much, much harder than programming with a single thread. When multiple threads access the same program data (Fields, static Fields, structs, etc.) - and indeed data from a DB - one can easily get intermittent problems which can be very hard to pin-point and to resolve. Extreme diligence needs to be employed when multiple threads should access some shared program data - and indeed data that resides in a DB - in a writing fashion! Debugging a multi-threaded program is also considerably more difficult than debugging a single-threaded program. Whole books are devoted to the topic of multi-threaded programming as multi-threading is a quite difficult discipline that is hard to master... | ||
==The Future: A Safe-to-use, Multi-threading-Enabled OpenPetra== | |||
That is the vision! When we will get to that stage is not certain, as the completion of other, more pressing OpenPetra features is higher on our agenda. | |||
Still, by having in mind how Co-ordinated DB Access works, we can try to make that vision become more and more a reality. | |||
In many cases the desired outcome can be reached by the automatic things that Co-Ordinated DB Access does for us, in other cases it will be easy to achieve with some manual efforts, and in some cases we will need to put considerable effort into solving multi-threading DB Access issues. | |||
''The recent introduction of the ability to [[Working with multiple DB Connections | work with multiple DB Connections]] opens up many possibilities to address such issues that we were previously not able to address!'' | |||
(Failing everything else, as a 'last resort' we can try to prevent the parallel-running of program code). | |||
==Questions?== | ==Questions?== | ||
In case you have questions regarding the 'Co-ordinated DB Access' feature please contact ChristianK, the developer of that feature. | In case you have questions regarding the 'Co-ordinated DB Access' feature please contact ChristianK, the developer of that feature. | ||
Latest revision as of 06:49, 29 September 2015
Co-ordinated DB Access: Overview
The Problem it Solves
Before we had Co-ordinated DB Access in place, users ran into various Exceptions when multi-threaded DB access occurred on the same DB Connection - no matter whether that multi-threaded DB access was done intentionally/deliberately by the programmer, or whether it happened as something that resulted 'accidentally' because of an action the user took (and which we didn't prevent from happening). Co-ordinated DB Access not only prevents that from happening, but also provides options to safely run program code that attempts to access the DB in parallel on the same DB Connection (however, multi-threading always brings some challenges, esp. with DB access - for details read the Challenges section).
The Solution
The primary solution was to make the TDataBase Class (OpenPetra's Database Access and Abstraction Layer) thread-safe (this got addressed by solving Bug #3852), meaning that we are employing pseudoparallel execution to prevent any 'collisions' on DB Access on the same DB Connection. That in itself prevented the Exceptions mentioned earlier from happening! (For 'true' parallel execution of DB Commands see Working with multiple DB Connections).
Building on that, ...
- provisions have been put in place to allow the OpenPetra software engineers to react programmatically to various new situations where the now co-ordinated DB Access can raise specific Typed Exceptions in case the desired 'parallel-ity' cannot be achieved automatically in a given situation (on a DB Connection that is shared by multiple Threads);
- provisions have been made in the client-side 'Unhandled Exception Handler' to automatically show 'friendly and helpful' messages to the user when the software engineers didn't react programmatically to various new situations (yet).
The automatic 'friendly and helpful' messages may well be enough for situations in which concurrent DB access operations aren't occurring often and where the user wouldn't be too annoyed to perform any retry attempts by themselves. Details
The ability to react programmatically to the various new situations exists to perform automatic retries 'under the hood', to allow for 'better' provisions for the user (e.g. to provide Retry/Cancel options), and to be able to prevent the user from taking certain actions in the first place that could (later) lead to the inability to take certain actions (e.g. disallowing the opening of a screen under certain circumstances because the particular circumstance would mean that any entered data might not be 'save-able' by the user later on). Details
Pseudoparallel Execution
What happens in our 'co-ordinated DB Access' is that we allow only one thread at any given time access to DB-related functionality that is exposed through the TDataBase Class when those threads are sharing the same DB Connection. That means that other threads that want to utilise the same DB Connection need to wait until the first thread has finished accessing the DB through the TDataBase Class (an automatic time-out time-out is in place to mitigate 'stalling' situations).
We need to do this because we can't offer 'true' parallelism on the same DB Connection. The reasons for that are:
- The ADO.NET DB driver model cannot maintain multiple active statements (commands) on a single DB Connection.
- (Well, for SQLServer and Oracle there is a specific solution {'Multiple Active Result Sets', | MARS}, but it isn't a standard feature of ADO.NET and not available for other RDBMS's).
- even the PostgreSQL RDBMS allows only one running DB Transaction per DB Connection!
For 'true' parallel execution of DB Commands see Working with multiple DB Connections!
Relation to Working with multiple DB Connections
Cf. this paragraph.
Details of the Implementation
What is Done Automatically And What Needs to be Handled Manually
Automatic (and Fully Transparent): Thread-safe DB Access through the TDataBase Class
Automatic Thread-Safety
The thread-safety is fully transparent to the software engineers, that is, the software engineers don't need to do anything to make sure it works, and don't even need to know how it works.
(For the curious: Thread-safety is achieved by using a SemaphoreSlim Object {FCoordinatedDBAccess} with a capacity of only one, two new Methods {WaitForCoordinatedDBAccess and ReleaseCoordinatedDBAccess}, and by calling those two Methods appropriately in all places where it is required to achieve thread-safety 'inside' an instance of the TDataBase Class across every functionality that this Class offers. For the even-more-curious: A Mutex or lock couldn't be used to achieve that since these aren't 'thread-agnostic', whereas a SemaphoreSlim is thread-agnostic. Also, a SemaphoreSlim is a very performant way to achieve thread-safety. {Details})
Automatic Time-out (Thread Stalling Prevention)
Suppose a thread that 'locks' an instance of the TDataBase Class (due to the thread-safety being in place) would run for a long time, or even 'stall' for some reason or the other, or get into an 'endless loop', and hence wouldn't release the 'lock' on that instance of the TDataBase Class. While none of these should happen (of course...), the consequence of any of this happening would be that all other threads of a user that were waiting for DB Access on that instance of TDataBase would be waiting to get access to the DB - for however long it takes for the first thread that 'grabbed the lock' to finish. In case the instance of TDataBase is the 'globally available' DBAccess.GDBAccessObj this situation would not only give the user the impression that 'OpenPetra isn't responding/has crashed', but would also mean they couldn't save any work that they haven't saved yet, which they might be able to do if we are able to offer them 'Retry/Cancel' options!
An automatic time-out is in place to help avoid those unwanted issues. This time-out applies not to the first thread (that 'locked' the instance of the TDataBase Class), but to any 'next' thread that wants to use that instance of the TDataBase Class and which has to wait. The time-out means that this waiting isn't 'indefinite', but ends after a set time-out, and hence the thread that ran into the time-out can perform some action. That action could be as simple as repeating the request for DB access or giving the user the opportunity to either continue waiting or cancel the operation that the user initiated.
Important: The time-out doesn't mean that a thread that wants to execute some action using the TDataBase Class has to wait until the automatic time-out has expired if another thread 'grabbed the lock' earlier on the same instance of TDataBase. Rather, the second thread will execute the action as soon as the first thread finishes its work and 'releases the lock'! Example: If the first thread 'grabs the lock', executes an action and 'releases the lock' within 4 seconds, a second (waiting) thread will be able to 'grab the lock' after those 4 seconds, and not just after the time-out expired!
When the time-out does expire, the TDataBase Class throws an Exception, EDBCoordinatedDBAccessWaitingTimeExceededException. Though a calling Method could catch this Exception specifically, it is more helpful to catch its Base Class, EDBAccessLackingCoordinationException. For details about this see this section.
Configuration (Optional): Automatic Time-out
The automatic time-out time can be configured. That configuration option has been introduced to prevent users from running into time-outs too often in situations where an OpenPetra Site has got a slower server than average OpenPetra Sites, or a higher concurrent user count than average OpenPetra Sites, or both. The value would be set to a higher number than the default in such situations.
The time-out value defaults to 3000 (=3.000 milliseconds, which equals 3 seconds) but can be changed by including the appSetting Server.DBWaitingTimeForCoordinatedDBAccess in the Server.config file. Testing has so far shown that 3.000 milliseconds is sufficient for situations where a 'not-very-fast' virtual test server is used on which limited numbers of users perform concurrent actions. That default could easily be changed in the future, should that become necessary (it is specified in the TDataBase Class Constructor).
Semi-Automatic: (DB-)Call Retries
The most common reaction to an automatic time-out should be a retry of getting the 'lock' on a given instance of the TDataBase Class (e.g. on the 'globally available' DBAccess.GDBAccessObj). The reason for that is that often the second or third attempt of getting this 'lock' on that instance succeeds (as many DB queries run only for a short time)! It would therefore not be very user-friendly to show a message to the user that the action that (s)he has taken could not be performed when an internal retry on that instance (which the user doesn't notice) can often succeed.
A new Class has been introduced to make it easy to program such DB call retries. The new Ict.Common.DB.TServerBusyHelper Class has got only one static Method, CoordinatedAutoRetryCall. Use this Method wherever you expect that the taking-out of a 'lock' on a given instance of TDataBase could time out as other things that run in parallel on that instance might have come first in taking a 'lock' out. For details about this see this section.
Configuration (Optional): Number of Retries
The number of retries that the TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall Method automatically performs can be configured. That configuration option has been introduced to prevent users from running into time-outs too often in situations where an OpenPetra Site has got a slower server than average OpenPetra Sites, or a higher concurrent user count than average OpenPetra Sites, or both. The value would be set to a higher number than the default in such situations.
The time-out value defaults to 3 (=3 retries) but can be changed by including the appSetting CoordinatedAutoRetryCallMaxRetries in the Client.config file (for controlling the number of retries when the TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall Method is used client-side) and/or the Server.config file (for controlling the number of retries when the CoordinatedAutoRetryCall Method is used server-side).
Automatic: Co-ordinated DB Access Exception Handling
The client-side 'Unhandled Exception Handler' presents 'stock messages' to users in case an Exception that derives from the EDBAccessLackingCoordinationException Exception makes it as far as that (that is, if a programmer didn't use the TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall Method and didn't catch it server-side or client-side). This is a much better option than letting the Exception escalate and showing the Unhandled Exception Dialog as a result of that, and it can work on its own in many, simpler, scenarios.
However, for complex OpenPetra operations, esp. ones where DB queries can take longer to run on a given instance of TDataBase (e.g. on the 'globally available' DBAccess.GDBAccessObj), custom code that reacts programmatically will need to be written in screens (or even server-side) to support the running of such features alongside Reports or Find screens, or to prevent users from launching such features in the first place - see this section for that.
Example of such an automatically-shown MessageBox:
--------------------------- OpenPetra Server Too Busy --------------------------- The OpenPetra Server is currently too busy to perform the requested action. (Reason: Waiting time for initiating exclusive data access exceeded.). Please wait a few seconds, then retry the action that you wanted to perform (if you had previously started a long-running action and this is not finished yet, you might need to wait until this is finished). If you have received this message while a screen was opened and that screen is left open then please don't try to use that screen! Rather, close it and try to open it again. --------------------------- OK ---------------------------
The '(Reason: XXX.)' part in those Messages can have different wording that helps a developer to know what has gone wrong (since the the Exception information is 'hidden' from the GUI):
- 'Reason: Waiting time for initiating exclusive data access exceeded.' – gets shown when
EDBTransactionBusyExceptiongets thrown. This will be the case when the caller called one of theBeginXXXTransactionMethods, but another DB Transaction (e.g. from running a Report) was already running on the sameTDataBaseinstance and the call cannot be satisfied because no second (=concurrent) DB Transaction can be started. - 'Reason: Failed to initiate shared data access.' – gets shown when
EDBTransactionIsolationLevelWrongExceptiongets thrown. This will be the case when the caller called one of theGetNewOrExistingXXXTransactionMethods, but another DB Transaction (e.g. from running a Report) was already running on the sameTDataBaseinstance and the call cannot be satisfied because of a mismatch of the 'IsolationLevel'. - 'Reason: Waiting time for data access exceeded.' – gets shown when the new
EDBCoordinatedDBAccessWaitingTimeExceededExceptiongets thrown. This will be the case when the caller called one of theGetNewOrExistingXXXTransactionMethods, but another DB Transaction (e.g. from running a Report) was already running on the sameTDataBaseinstance, and – while there wasn't a mismatch of the IsolationLevel – the second call timed out because it could not get exclusive access to the DB Connection that is held open by thatTDataBaseinstance. This will be the case when the original call to the DB (on the sameTDataBaseinstance) takes longer than the time-out (3 seconds by default).
Additionally, when the appSetting 'Client.DebugLevel' is set to a minimum of 3 in the Client.config file the Unhandled Exception handler also logs the full Exception details to the Client.log. This is useful for detailed checks by the developer. At that DebugLevel the developer also gets information in the Client.log about the various retry attempts, and if they were exceeded, for cases where screens handle those using the in an automatic retry fashion by means of the TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall Method. Examples of screens/screen parts for the latter: the Partner Find/Partner Info Panel, the Partner Edit screen and the Maintain Extracts screen (when opening a Partner from the latter). The Client-side Cacheable DataTable Manager utilises TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall, too.
Examples
Apart from the example that is shown in the bullet list below there aren't any specific example actions that you could take to make the automatic 'stock messages' come up; rather, they will come up when an EDBAccessLackingCoordinationException Exception makes it as far as the Unhandled Exception Handler! (You can try to 'provoke' such an occurrence, though, by following the instructions here.)
Reproducible example for a BeginXXXTransaction call 'not going through' on the 'globally available' DBAccess.GDBAccessObj:
- Start the 'Partner by Subscription' Report from Partner Module -> Reports with a 'popular' Subscription (e.g. 'AFRIKAANS' on the SA DB; that will run for quite some time).
- While that runs, go to Partner Module -> Partners and click 'Add New Person'. The screen opens fine, but on clicking 'OK' the user is presented with an automatically-shown MessageBox (see example above). On clicking 'OK' on that MessageBox, the user is back in the Main Menu (while the Report happily continues to calculate!). That also works when 'New Partner' is initiated e.g. from the Partner Edit screen, in that case one is back on the Partner Edit screen that you pressed 'New Partner' on.
- We might be able to improve on this by keeping the user in the 'New Partner' Dialog (rather than closing this and returning him/her to wherever (s)he came from), but that is something that needs extra assessment and specific programming.
- Notes
- In this case a
BeginXXXTransactioncall with IsolationLevel 'Serializable' needs to be used because only that can guarantee that the Partner Key that gets generated will exist exactly once in the DB! - The solution to overcome this particular issue is to use the Working with multiple DB Connections feature in the Partner Edit UIConnector (
TPartnerEditUIConnectorClass)!
- In this case a
Manual: Co-ordinated DB Access Exception Handling
Manual handling of Exceptions that either stem from co-ordinated DB Access, or from calling one of the BeginXXXTransaction Methods when a DB Transaction is already running is done in several ways:
Utilising the TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall Method
Usage: Performing 'silent' and automatic retries for 'getting a lock' on an instance of the TDataBase Class (e.g. on the 'globally available' DBAccess.GDBAccessObj TDataBase instance). Use this where you expect (or know) that multi-threaded DB Access on an instance of the TDataBase Class may potentially occur due to user actions or deliberate programmatic means.
What The Method Does
The TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall Method will automatically execute program code that resides in a Delegate at least once, but up to 'n' times when required. It will repeat the execution of that program code in case either the EDBTransactionBusyException, the EDBCoordinatedDBAccessWaitingTimeExceededException or the EDBAttemptingToWorkWithTransactionThatGotStartedOnDifferentThreadException (see here for the latter) Exceptions get thrown (all those Exceptions derive from EDBAccessLackingCoordinationException).
Retry Strategy
- Repeats are performed up to a set number of times (how often it is repeated at most is dermined by a default value {3} or the optional appSetting
CoordinatedAutoRetryCallMaxRetriesin the Client.config or Server.config file. Details); - The Method doesn't wait between the retries but issues a retry attempt immediately after one of the Exceptions mentioned in the previous paragraph gets thrown;
- By default the Method doesn't do anything when the number of repeats got exceeded, but it can be instructed to throw an
EDBAutoServerCallRetriesExceededExceptionException in that case by setting the optional ArgumentAWhenNotSuccessfulThrowSpecialExceptiontotrue. That is normally not necessary, though, as you will find out in the next section.
That Method can be used client-side or server-side. While it does the same on both 'sides', the scenarios in which you would want to use it client-side or server-side differ.
- Client-side
- Usage: Performing retries 'silently'. In case the retry attempts were exceeded the user should get told that either...
- the action the user wanted to take cannot be performed because the server is busy at the moment and that the user will need to try that action again at a later time.
- the action the user wanted to take cannot be performed because the server is busy at the moment and the user is given the choice to either retry or to cancel the action (this is of course more user-friendly, but it might not always be easy to implement).
- Usage: Performing retries 'silently'. In case the retry attempts were exceeded the user should get told that either...
- Server-side
- Usage: Performing retries 'silently'. In case the retry attempts were exceeded an appropriate action should get taken by the server-side code.
How to Use The Method
This is best explained by showing client-side example code:
bool ServerCallSuccessful = false;
IMyUIConnector UIConnector = null;
...
Ict.Common.DB.TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall("Some Context (only used for logging)", ref ServerCallSuccessful,
delegate
{
UIConnector = TRemote.SomeServerCall();
ServerCallSuccessful = true;
});
if (!ServerCallSuccessful)
{
// ServerCallRetries must be equal to the maximum number of retries when we get here!
if (TServerBusyHelperGui.ShowServerBusyDialogWhenOpeningForm(Catalog.GetString("Some Context That is Meaningful to the User Here")) == DialogResult.Retry)
{
// In the simplest case: recursively call the Method that this code snippet is in...
}
return; // Also gets executed when the user chooses 'Cancel' in the displayed dialog!
}
// Further program code continues execution only if there were no retry attempts, or if the last retry attempt succeeded.
Important: The code section inside the Delegate code block is responsible for setting ServerCallSuccessful = true;, as only this section can know whether the server call went through OK, or not. The Ict.Common.DB.TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall Method evaluates the value of this Variable and will issue retries until either the Variable's value becomes true or the number of maximum retries has been exceeded.
Once the Ict.Common.DB.TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall returns, the program code that called this Method must evaluate the value of the ServerCallSuccessful Variable to find out whether the server call succeeded (with, or without retries) or failed and needs to take appropriate action.
As for the action to take when the server call didn't succeed: The TServerBusyHelperGui Class has been introduced to provide a small library that facilitates the uniform display of MessageBoxes and retry/cancel options. Have a look at the available Methods and choose the one that you want to implement in your code section.
If you call the TServerBusyHelperGui.ShowServerBusyDialogWhenOpeningForm Method the user has the choice between retry or cancel. To make the 'retry' option viable you might need to refactor the server call out of existing code into a Method of its own so it can get called recursively for the retries.
A good place on the client side in which to put the call to Ict.Common.DB.TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall is the Form.Load event. There the cancellation of the opening of the form might be easiest as well.
Any server-side use of the Ict.Common.DB.TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall is very similar to what is shown above, though the TServerBusyHelperGui Class isn't available server-side.
The Ict.Common.DB.TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall Method has two optional Arguments, bool AWhenNotSuccessfulThrowSpecialException and string AExceptionMessage. The program code as explained above is rather elegant, but in case you rather want an Exception to be raised when the retry attempts were exceeded, you can make the Method raise the Typed Exception EDBAutoServerCallRetriesExceededException by supplying true to the AWhenNotSuccessfulThrowSpecialException Argument. If you do that, then setting AExceptionMessage will allow passing a Message to that Exception.
Catching EDBAccessLackingCoordinationException Server-side
EDBAccessLackingCoordinationException is the Base Class from which the following Exceptions derive:
EDBTransactionIsolationLevelWrongExceptionEDBTransactionBusyExceptionEDBCoordinatedDBAccessWaitingTimeExceededExceptionEDBAutoServerCallRetriesExceededException
If you have an Exception handler in place in server-side code that logs all Exceptions and then throws the Exception up the call stack you will likely not want to log the occurrence of any of the above Exceptions as the client side can deal with those in a good way (either you handle it programmatically or the 'Unhandled Exception Handler' will show a 'stock message' as the last resort). To prevent any of those Exceptions from getting logged, add a code section like the following before the catch (Exception) code section:
catch (EDBAccessLackingCoordinationException)
{
// don't log this Exception - the Client knows how to deal with it.
throw;
}
Examples / Implementations
As per March 2015 the following places exist that utilise the TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall Method:
Client Side
This section needs reviewing as we expect that we will use multiple DB Connections in several of the places mentioned!
- Partner Edit screen (Method 'GetPartnerEditUIConnector' in file \csharp\ICT\Petra\Client\MPartner\Gui\PartnerEdit.ManualCode.cs);
- Maintain Extracts screen - when opening a Partner for editing (Method 'EditPartner' in file \csharp\ICT\Petra\Client\MPartner\Gui\Extracts\UC_ExtractMaintain.ManualCode.cs);
- Partner Find screen/Partner Info Panel (Method 'FetchDataFromServer' in file \csharp\ICT\Petra\Client\MPartner\Gui\UC_PartnerInfo.cs [that Method is launched only from a Timer, i.e. runs in a separate client-side Thread!]);
- 'TSystemDefaults.GetSystemDefault' Method in file \csharp\ICT\Petra\Client\app\Core\SystemDefaults.cs;
- 'TFrmMainWindowNew.UpdateSubsystemLinkStatus' Method in file \csharp\ICT\Petra\Client\app\MainWindow\MainWindowNew.ManualCode.cs.
- this gets called every time a users switches to the Finance Module in the Main Menu. The retries are there as the user might do that while other things are running against the DB (e.g. a Partner Find search operatin, or a FastReport).
The Client-side CacheableDataTable Manager (TDataCache) utilises TServerBusyHelper.CoordinatedAutoRetryCall, too (two overloads of the Method 'GetCacheableDataTableFromPetraServer' in file \csharp\ICT\Petra\Client\app\Core\Cache.cs).
Server Side
This section needs reviewing as we expect that we will use multiple DB Connections in several of the places mentioned!
- 'TReportingDbAdapter.RunQuery' Method in file \csharp\ICT\Petra\Server\lib\MCommon\Main.cs;
- This is used by FastReports for executing arbitrary SQL statements
- 'TSystemDefaults.GetSystemDefaults' Method in file \csharp\ICT\Petra\Server\lib\MSysMan\SystemDefaults.cs.
Extra Things that You Need to Know
How to Find Out if (Automatic) Co-ordinated DB Access Will Yield Acceptable Behaviour In a Given Circumstance
It can be trick to try to exercise the program code that you have written manually for the retrying of server calls that make DB calls, as it will only run when the co-ordinated DB Access retries have been 'used up' on an instance of the TDataBase Class (e.g. on the 'globally available' DBAccess.GDBAccessObj TDataBase instance).
Connecting the PetraServerConsole.exe to a DB that is remotely located rather than on your local development machine will greatly increase the likelihood that your code will get run.
Other ways of 'helping' that to occur is to use either one, or both, of the following appSettings:
- Place
CoordinatedAutoRetryCallMaxRetriesin the appropriate config file (Client.config or Server.config) and set its value to '1', meaning only one call attempt is made, and if this times out, no further retries will be made.- This will raise the likelihood of running into a time-out and the calling Method's code path that deals with non-successful server calls will be more likely run because of this. (Details)
- Place
Server.DBWaitingTimeForCoordinatedDBAccessin the Server.config file and setting its value to something quite low, such as 50 (the default is 3000). The value specifies the number of milliseconds a second thread will wait for the first thread to be releasing the 'lock' on an instance of theTDataBaseClass (e.g. on the 'globally available'DBAccess.GDBAccessObjTDataBaseinstance).- The lower the number, the more the likelihood of running into a time-out is raised and the calling Method's code path that deals with non-successful server calls will be more likely run because of this. (Details)
Programming / Debugging
- '
return' statements can be placed inside the code section that becomes a 'delegate', but they leave that code section and not the Method that contains the Automatic Transaction, and only a 'return;' statement that doesn't return a value is possible. - The code section that becomes a 'delegate' must not use '
ref' or 'out' Arguments of the Method that they are contained in (as that will result in the C# Compiler Error CS1628)- Solution: Declare a local Variable and assign the value of a '
ref' or 'out' Argument to it, then use the local Variable in the code section that becomes a 'delegate'. (In case of a 'ref' Argument you will likely need to assign the value of that Variable to the Argument before you leave the Method in order for the Argument to have the same value than the Variable.)- Note: By assigning the value to the local Variable, the local Variable points to the same address in memory than the value of the '
ref' or 'out' Argument - hence they are referencing the same instance of the object. This is an implementation detail of C# (this is the same as with Java).
- Note: By assigning the value to the local Variable, the local Variable points to the same address in memory than the value of the '
- Solution: Declare a local Variable and assign the value of a '
- Debugging:
- There is some extra code to step through if one single-steps into/out of a code section that becomes a 'delegate' (compared to the code that follows the try/finally Policy and that doesn't use the Automatic DB Transaction Handling)
- Solution if you don't want that to happen:
- Use 'Step over' (F10) instead of 'Step into' (F11) on those code lines.
- In case you use SharpDevelop: Put a breakpoint on the line in the delegate from where on you want to investigate as F10 steps over the entire code that is contained in the delegate if this isn't done!
- Solution if you don't want that to happen:
- As the software engineer can step into the program code of any of the new Methods that handle the automatic DB Transactions (s)he can see as to why the DB Commits/DB Rollbacks happen!
- When using SharpDevelop 5 to halt debug execution at the 'Automatic DB Handling' scope the whole code section is highlighted in yellow - very helpful, as the scope of the DB access logic is easily seen through that :-)
- There is some extra code to step through if one single-steps into/out of a code section that becomes a 'delegate' (compared to the code that follows the try/finally Policy and that doesn't use the Automatic DB Transaction Handling)
- Logging
- The logging facilities of the
TDataBaseClass have been improved and extended when Co-ordinated DB Access got implemented.- Specifically, Thread ID's, Thread Names (where available) and AppDomains get logged in all situations where one needs that information while debugging program code that deals with multiple threads. Also, StackTraces have been added here and there to help developers figure out what happens.
- At the new DebugLevel 11 even more StackTraces get logged, namely whenever a 'lock' is taken out on an instance of the
TDataBaseClass (e.g. on the 'globally available'DBAccess.GDBAccessObjTDataBaseinstance), and when it is released. You will find that this is extremely verbose and hence it should only be used while debugging very tricky program code that deals with multiple threads.
- The logging facilities of the
Challenges
GetNewOrExistingXXXTransaction Must be Used When Multiple Threads Need 'Parallel' DB Access
When multiple threads are to be running side-by-side and both will be accessing the DB with the same instance of the TDataBase Class (e.g. using the 'globally available' DBAccess.GDBAccessObj TDataBase instance), all code sections in both threads' server-side program code must start or re-use DB Transactions by calling GetNewOrExistingXXXTransaction. This means that none of the code sections in both threads' server-side code must call BeginXXXTransaction. The obvious reason for that is that we can't start a second DB Transaction as we are employing pseudoparallel execution. (For 'truly' parallel DB Transaction and true parallel execution of DB Commands, which get around that limitation, see Working with multiple DB Connections).
IsolationLevels Need To be Fitting When Multiple Threads Need 'Parallel' DB Access
In addition to what the previous paragraph stated, all code sections in both threads' server-side program code must be using the same IsolationLevel in the GetNewOrExistingXXXTransaction calls, as otherwise an EDBTransactionIsolationLevelWrongException Exception will be thrown at some point by one of the GetNewOrExistingXXXTransaction calls. (For 'truly' parallel DB Transaction and true parallel execution of DB Commands, which get around that limitation, see Working with multiple DB Connections).
Performance Considerations
As we are employing pseudoparallel execution to prevent any 'collisions' on DB Access on the same instance of the TDataBase Class (e.g. on the 'globally available' DBAccess.GDBAccessObj TDataBase instance), you must expect that DB access is a limiting factor in how 'parallel' multiple threads can actually run, even on servers that have multiple processors! (For 'truly' parallel DB Transaction and true parallel execution of DB Commands, by which we can get around that 'bottleneck', see Working with multiple DB Connections!)
How much the pseudoparallel execution will impede the performance of multiple threads that are accessing the DB with the same instance of the TDataBase Class will depend heavily on how much the individual threads utilise DB access vs. how much they 'compute', i.e. perform non-DB-access-related operations. If both threads access the DB heavily at roughly the same times, the execution speed of the threads will be heavily impeded as only one thread a time gets access to the DB. If, however, the threads do quite some computations and only some DB access (which ideally doesn't occur at roughly the same times) then the performance of individual multiple threads will not be impeded and operations involving multiple threads can well yield advantages over operations that consist of a single thread on servers that have multiple processors.
This also affects the user: When a user starts multiple Reports in parallel (e.g. just before going on lunch break), the combined time that both Reports take to calculate might be higher, or lower, than if they were started individually one-after-the-other. This will depend on how many DB access operations will 'compete' over DB access on the same instance of the TDataBase Class (e.g. on the 'globally available' DBAccess.GDBAccessObj TDataBase instance) - and of course also whether the server on which the PetraServerConsles.exe process runs has got multiple processors, or only one processor...
Stopping/Cancellation of Multiple Running Queries
Reference: Stopping of Running DB Queries
This section needs reviewing as we expect that we will use multiple DB Connections in several of the places mentioned!
When multiple DB actions are running in a pseudoparallel fashion on the same instance of the TDataBase Class (e.g. using the 'globally available' DBAccess.GDBAccessObj TDataBase instance), the behaviour of a cancellation action is as follows:
- Pressing 'Cancel' on the Partner Find screen while a FastReport is running, or pressing 'Cancel' on a FastReport Report Window while Partner Find is running can work when the particular FastReport that runs has proper error handling and cancellation handling; the 'Income Expense Report' does have that (at least in some of the main areas of the report code...). When it works, both the FastReport and the Find screen stop their queries at the same time. By the time of writing this we are not sure why this happens, but this might be down to the Npgsql ADO.NET PostgreSQL driver, or even down to PostgreSQL.
- Pressing 'Cancel' on the Partner Find screen while a FastReport is running can in certain circumstances also break OpenPetra, at least at the time of writing. This will need further investigation, but again this might not be something that we can provide safely in the future (hence we might need to prevent that in the GUI 'somehow'). However, getting this to work is probably not very high on our list of things that we will implement in the nearer future...
Running Multiple XML Reports in Parallel: To be Investigated Further
It is at present not possible to start another XML Report (=non-FastReport) while a XML Report is already calculating.
The one reason for that has been identified so far is that our Logging framework (which is used for the output to the StatusBar) isn’t thread-safe and any such attempt results in a This has been fixed by ChristianK (this was Bug #4489)!
NullReferenceException for that reason.
That needs to be looked into specifically.
Once that is solved (is is now!) it is thought that we will likely encounter further 'stumbling blocks' for parallel XML Report runs, though (one example: Bug #4481). This will need further investigation, but this might not be something that we can provide safely in the future (hence we might need to prevent that in the GUI 'somehow'). However, getting this to work is probably not very high on our list of things that we will implement in the nearer future...
Running multiple FastReports in Parallel
This section needs reviewing as we expect that we will be able to utilise a separate DB Connection for each FastReport Report instance (see Working with multiple DB Connections)!
In principle multiple FastReport Reports can be run at the same time.
- ChristianK succeeded in running the Finance Module -> General Ledger -> 'Income Expense Statement' Report and the 'Excecutive Summary' Report in parallel.
- This might well not work with all kinds of combinations of FastReports - thorough Exception handling in the Reports' program code (and Cancellation handling, too, in case the 'Cancel' Button gets pressed on the Report Form or on another Form that has got a 'Cancel' button) is a must for that to work properly!
Multi-threading: General Advice
General caution/advice: Programming with multiple threads is always much, much harder than programming with a single thread. When multiple threads access the same program data (Fields, static Fields, structs, etc.) - and indeed data from a DB - one can easily get intermittent problems which can be very hard to pin-point and to resolve. Extreme diligence needs to be employed when multiple threads should access some shared program data - and indeed data that resides in a DB - in a writing fashion! Debugging a multi-threaded program is also considerably more difficult than debugging a single-threaded program. Whole books are devoted to the topic of multi-threaded programming as multi-threading is a quite difficult discipline that is hard to master...
The Future: A Safe-to-use, Multi-threading-Enabled OpenPetra
That is the vision! When we will get to that stage is not certain, as the completion of other, more pressing OpenPetra features is higher on our agenda.
Still, by having in mind how Co-ordinated DB Access works, we can try to make that vision become more and more a reality. In many cases the desired outcome can be reached by the automatic things that Co-Ordinated DB Access does for us, in other cases it will be easy to achieve with some manual efforts, and in some cases we will need to put considerable effort into solving multi-threading DB Access issues.
The recent introduction of the ability to work with multiple DB Connections opens up many possibilities to address such issues that we were previously not able to address!
(Failing everything else, as a 'last resort' we can try to prevent the parallel-running of program code).
Questions?
In case you have questions regarding the 'Co-ordinated DB Access' feature please contact ChristianK, the developer of that feature.